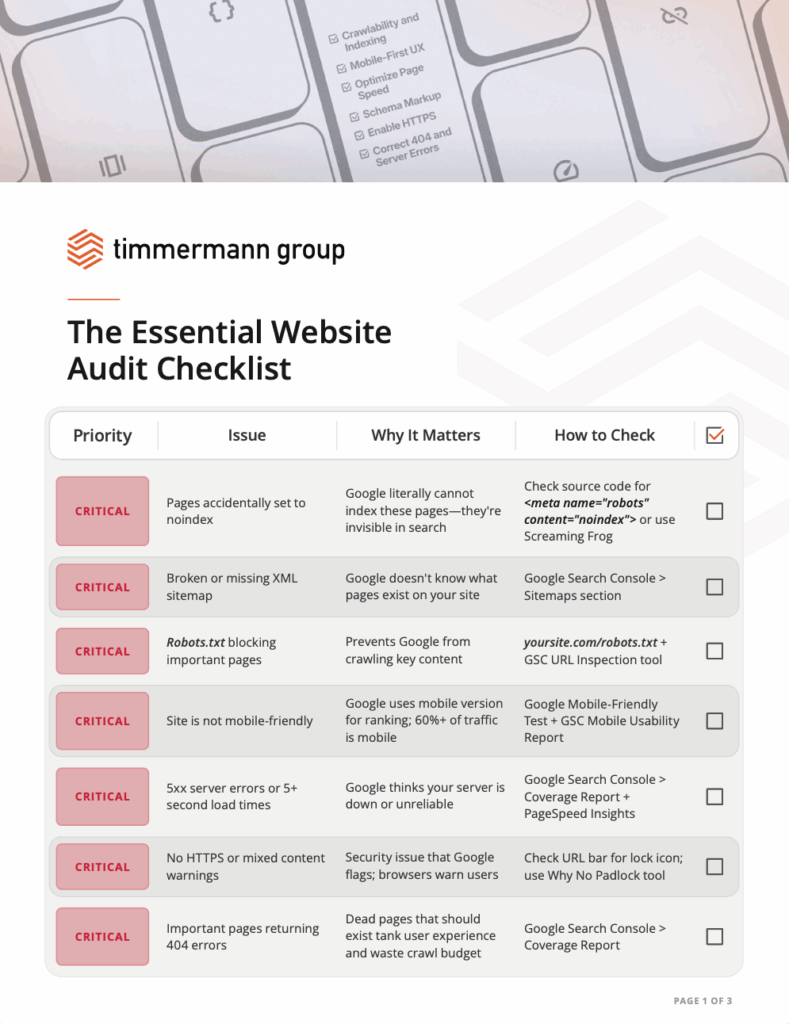
The Essential Website Audit Checklist: What Actually Matters in 2026
There’s a lot of data you can pull from website audits. Like, a lot. But here’s what I’ve learned after years of doing this work; most don’t actually impact your rankings.
The issues you need to worry about are the ones blocking Google from seeing your content. Pages accidentally set to noindex. JavaScript that hides your content from crawlers. Site speed so slow Google thinks your server is down.
Everything else? Sure, it matters. But this guide focuses on the stuff that can kill your traffic overnight.
Make Sure Google Can Actually Find Your Pages
First question: Can search engines even find your pages? If not, nothing else matters. Google can’t rank pages it can’t see. So before you optimize anything, make sure crawlers can find and index your content.
Understanding crawlability & indexing
Crawlability is whether Google’s bots can access and navigate your site. Indexing is whether Google can store and retrieve your pages to show them in search results. Think of it like this: crawlability is whether Google can walk through your front door and explore your house. Indexing is whether Google can remember what it saw and tell other people about it.
Common technical problems to watch for
Common crawlability problems include robots.txt files that accidentally block important pages, broken internal links that create dead ends, and redirect chains that exhaust Google’s crawl budget before reaching your content.
Indexing issues often show up as noindex tags on pages you want ranked, canonical tags pointing to the wrong URLs, or content hidden behind JavaScript that Google can’t process.
Why this affects your visibility
Here’s the bottom line: if Google can’t crawl your pages, they won’t get indexed. If they’re not indexed, they can’t rank. You could have the best content in the world, but if Google never sees it, you might as well not have published it at all.
How to audit your crawlability & indexing
XML Sitemap
Your XML sitemap is essentially a roadmap of your site for search engines. It tells Google which pages exist and which ones you consider most important. In 2026, with sites becoming increasingly complex and dynamic, a proper sitemap isn’t optional—it’s essential.
Your sitemap should include only the pages you want indexed. Don’t include pages with noindex tags, redirected URLs, or pages blocked by robots.txt. That just confuses search engines and wastes crawl budget.
How to Implement
Most modern CMS platforms (WordPress, Shopify, Wix) generate sitemaps automatically. If yours doesn’t, plugins like Yoast SEO or RankMath can create one for you. Once you have a sitemap, submit it through Google Search Console under the Sitemaps section.
Keep it updated. When you add new pages or remove old ones, your sitemap should reflect those changes. Most automatic sitemap generators handle this, but it’s worth checking periodically.
Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file tells search engines which parts of your site they can access and which are off-limits. The problem is, many sites accidentally block important pages.
Check your robots.txt file by visiting yoursite.com/robots.txt. Look for “Disallow” directives that might be blocking pages you want indexed. Common mistakes include blocking CSS or JavaScript files that Google needs to render your pages properly, or accidentally blocking entire sections of your site.
You can test your robots.txt file in Google Search Console under the URL Inspection tool to see if specific URLs are blocked.
Your Site Needs to Work on Phones
Why mobile-first indexing matters
Mobile devices account for over 60% of all web traffic. And Google now predominantly uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. If your site doesn’t work on a smartphone, you’re alienating the majority of your potential audience before they even read your first paragraph.
What makes a site truly responsive
Responsive design isn’t about making things smaller. A truly mobile-friendly site includes:
- Touch-friendly navigation with adequately sized buttons and links (Google recommends at least 48×48 pixels for tap targets)
- Readable text without zooming, typically 16px or larger for body copy
- Content that fits the screen without requiring horizontal scrolling
- Fast-loading images optimized for mobile bandwidth
- Simplified navigation that works with thumbs, not just mouse cursors
Testing your mobile experience
Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test
Head to Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool and enter your URL. It’ll show you exactly how Googlebot sees your mobile site and flag critical issues. If Google says your site isn’t mobile-friendly, that’s a red flag you need to address immediately.
Google’s Mobile Usability Report
Inside Search Console, check the Mobile Usability report under the Experience section. This shows you specific pages with mobile issues like text that’s too small, content wider than the screen, or clickable elements too close together. The beauty of this report is that it shows you real problems Google has encountered while crawling your site.
Manual Review on Devices
Don’t skip this step. Open your site on actual phones and tablets, both iOS and Android if possible. Use Chrome’s DevTools to test different screen sizes. Click through your navigation, fill out forms, and try to complete key user actions. You’ll often discover usability issues that automated tools miss, like a form that’s technically responsive but practically unusable on a small screen.
Help Search Engines Understand Your Content
Schema markup is code you add to your website that helps search engines understand your content better. Instead of just reading text and guessing what it means, schema explicitly tells search engines “this is a recipe,” “this is a person’s job title,” or “this is a product price.”
Why schema markup matters more than ever in 2026
Zero-click searches & rich results
Zero-click searches, where users get their answer directly on the search results page without clicking through to a website, have made structured data even more important in 2026. When your content has proper schema markup, you’re more likely to appear in featured snippets, knowledge panels, and rich results.
Yes, this sometimes means fewer clicks to your site sometimes. But it also means you own things like the AI overview and “people also ask box.” This helps establish authority even if users don’t click through. And for transactional queries, rich results with star ratings, prices, and availability can actually increase click-through rates.
How search engines think about entities
Modern search engines prioritize entities (people, places, things, and concepts) over individual keywords. Schema markup helps search engines understand the entities on your page and how they relate to each other.
When you mark up a local business with schema, you’re not just saying “here’s a business name and address.” You’re telling Google about an entity with a specific location, operating hours, services offered, and relationships to other entities like the people who work there or the products they sell. This deeper understanding helps search engines match your content to complex, conversational queries.
In practical terms, this means using schema markup like Organization, LocalBusiness, Person, Product, Article, FAQPage, and HowTo depending on your content type. Tools like Google’s Rich Results Test can show you if your schema is implemented correctly.
Every Second Counts When It Comes to Page Speed
We already covered how Google now uses the mobile version of your site for indexing. But beyond rankings, think about your own behavior. When was the last time you waited patiently for a slow website to load? Most users bounce within three seconds if a page doesn’t load. Site speed also ties into Google’s E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). A slow, clunky website signals poor quality and undermines trust. If your site feels neglected or unprofessional, why would users trust your expertise?
Tools to measure your site speed
- PageSpeed Insights provides both lab data and real-world field data from actual users. It shows your Core Web Vitals scores and prioritizes the fixes that will make the biggest impact.
- GTmetrix gives you a detailed waterfall view of how your page loads, helping you identify specific resources slowing things down.
- Google Search Console’s Core Web Vitals report shows you which pages on your site are struggling, based on real user data. This is gold because it tells you where to focus your efforts.
What to look for in your speed reports
Once you run these tests, you’ll get a list of recommendations. Here’s what to look for:
Unoptimized Images
This is the most common culprit. Large, uncompressed images can account for 50-70% of a page’s total weight. Compress images before uploading, use modern formats like WebP, and implement lazy loading so images only load as users scroll to them.
Render-Blocking Scripts/CSS
When JavaScript or CSS files block your page from rendering, users see a blank screen while they wait. Move non-critical CSS and JavaScript to load asynchronously or defer their loading until after the main content appears.
Server Response Time
If your server takes forever to respond (anything over 600ms is problematic), you might need better hosting. Cheap shared hosting often can’t handle traffic spikes or complex queries efficiently. Consider upgrading to better hosting or implementing a content delivery network (CDN).
Caching
Caching stores static versions of your pages so they don’t need to be rebuilt from scratch every time someone visits. Browser caching, server-side caching, and CDN caching all work together to dramatically improve load times for repeat visitors.
Excessive Plugins or Code
Every plugin or third-party script adds weight to your site. That social media feed widget? It might be loading dozens of requests. Audit your plugins regularly and remove anything you’re not actively using. For critical third-party scripts like analytics, consider loading them asynchronously.
Download Our Free Website Audit Checklist
A website audit checklist is a starting point, not the solution.
Our SEO services include monthly technical audits to catch issues before they hurt your rankings, plus an in-house dev team that implements fixes immediately. No waiting, no back-and-forth, no wondering if it’s done right. Schedule a free consultation to learn how Timmermann Group can help fix issues with your website that allow it to rank, convert, and deliver results for your business.