Schema Markup: The Complete Guide 2026
In 2026, search engines process over 8.5 billion queries daily. While most websites compete for attention in crowded search results, those using structured data as a part of their SEO strategy enjoy enhanced visibility through rich snippets, knowledge panels, and improved AI search integration.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about schema markup in 2026, from basic concepts to advanced implementation strategies. You’ll learn how to add schema markup to your web pages, understand different types of schema markup, and measure the impact on your search results performance.
Key Takeaways
- Schema markup drives 20-30% higher click-through rates by triggering rich results with star ratings, prices, and enhanced displays that make your listings stand out in search results
- Five essential schema types maximize SEO impact: Organization schema for brand recognition, Local Business for location visibility, Product schema for ecommerce, Article schema for content, and Review schema for trust signals
- JSON-LD is the preferred implementation method because it separates structured data from HTML content, making it easier to maintain and integrate with content management systems like WordPress
- AI search integration makes schema markup critical for 2026 as Google’s Search Generative Experience and voice assistants rely heavily on structured data to understand content relationships and provide accurate responses
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is structured data code added to HTML that helps search engines understand webpage content more effectively. Rather than relying on complex algorithms to interpret page content, schema markup provides explicit clues about what information means and how different elements relate to each other.
The foundation of schema markup lies in the Schema.org vocabulary, created collaboratively by Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex in 2011. This standardized format allows search engines to process web page information with greater accuracy and confidence, transforming unstructured content into machine-readable data using key-value pairs.

When you implement schema markup correctly, you’re essentially providing a roadmap for search engines to navigate your content. Instead of guessing what your page is about, search engines can identify specific entities, their properties, and relationships with surgical precision. This enhanced understanding enables search engines to deliver richer, more relevant search experiences to users.
The core principle behind schema markup involves defining entities (distinct things like people, products, or events), their properties (attributes like names, dates, or prices), and relationships between different elements. This structured approach helps search engines build comprehensive knowledge graphs that power everything from featured snippets to voice search responses.
Understanding how schema markup works is essential for any website owner serious about search engine optimization. By providing as much relevant information as possible through structured data, you enable search engines to present your content in the most favorable light possible.
Why Schema Markup is Critical for SEO Success
Schema markup has become indispensable for SEO success because it directly influences how search engines display your content in search results. Websites with properly implemented structured data see click-through rate improvements of 20-30% compared to standard listings, according to industry studies and case studies from leading SEO agencies.
The primary benefit of adding schema markup lies in its ability to trigger rich results that make your listings stand out in search engine results pages. These enhanced displays include star ratings, price information, availability status, and other compelling details that encourage users to click through to your website.
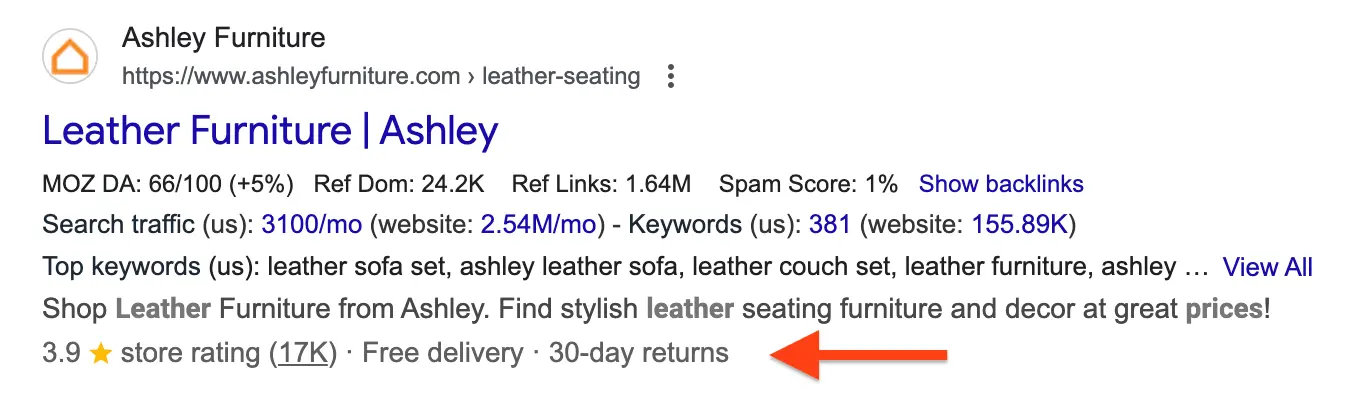
Beyond visual enhancements, schema markup helps search engines understand web pages’ content context and relationships between entities on your web pages. This improved comprehension leads to better matching of your content with relevant search queries, potentially improving your rankings for target keywords and related terms.
As AI and voice search continue to evolve in 2026, schema markup becomes even more crucial for optimization. Generative AI search engines like Google’s Search Generative Experience rely heavily on structured data to understand content relationships and provide accurate information in AI-generated responses. Websites without schema markup risk being overlooked in these emerging search formats.
Schema markup also builds content knowledge graphs that support various search features. When you implement organization schema or local business schema, you’re helping search engines create comprehensive entity profiles that can trigger knowledge panels, improve local search visibility, and enhance brand recognition across multiple search touchpoints.
The competitive advantage of schema markup cannot be overstated in today’s search landscape. While many websites still lack proper structured data implementation, early adopters enjoy improved visibility, higher click-through rates, and better positioning for emerging search technologies.
Essential Types of Schema Markup for Websites
The Schema.org vocabulary includes over 800 different schema types, but most websites benefit from implementing a core set of high-impact schemas. Understanding which types of schema markup to prioritize depends on your business model, content strategy, and target audience needs.
The most effective approach involves starting with foundational schemas that establish your website’s entity relationships, then expanding to content-specific schemas that enhance individual pages. This systematic implementation ensures maximum impact while maintaining code quality and avoiding potential markup issues.
Organization Schema
Organization schema defines your business entity with essential details like name, logo, address, and contact information. This foundational markup enables knowledge panel appearances in Google search results and establishes your brand as a recognized entity in search engine knowledge graphs.
Implementing organization schema correctly involves more than basic contact details. Include sameAs properties linking to your official social media profiles, specify your organization type (Corporation, LocalBusiness, NGO, etc.), and provide comprehensive contact details including phone numbers and physical addresses.
Here’s a complete JSON-LD example for organization markup:
{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Organization", "name": "Example Company", "url": "https://www.example.com", "logo": "https://www.example.com/logo.png", "address": { "@type": "PostalAddress", "streetAddress": "123 Business Street", "addressLocality": "City", "addressRegion": "State", "postalCode": "12345", "addressCountry": "US" }, "contactPoint": { "@type": "ContactPoint", "telephone": "+1-555-123-4567", "contactType": "customer service" }, "sameAs": [ "https://facebook.com/examplecompany", "https://twitter.com/examplecompany", "https://linkedin.com/company/examplecompany" ] }
Organization schema serves as the foundation for other schema types on your website. When you establish clear organizational identity through structured data, you create a framework that supports product markup, local business markup, and other specialized schemas across your entire website.
Local Business Schema
Local business schema extends organization schema with location-specific details like opening hours, service areas, and customer reviews. This specialized markup is critical for local SEO and Google Business Profile optimization, directly impacting your visibility in local search results and Google Maps.
Effective local business schema includes detailed operational information that helps users make informed decisions. Specify exact opening hours for each day of the week, include seasonal variations if applicable, and mark special circumstances like holiday closures or temporary service changes.
The geo property within local business schema helps search engines understand your precise location, which is essential for “near me” searches and location-based query matching. Include both latitude and longitude coordinates for maximum accuracy, especially if your business operates from multiple locations.
For service-based businesses, the areaServed property defines your coverage area, helping search engines match your business with location-specific queries. This is particularly important for businesses that serve customers beyond their immediate physical location.
Review schema integration within local business markup can display star ratings and review summaries directly in search results. However, ensure compliance with Google’s review snippet guidelines to avoid penalties or loss of rich result eligibility.

Product Schema
Product schema displays essential product details like price, availability, and customer reviews in search results, making it indispensable for ecommerce websites and affiliate marketers. This structured data markup directly influences purchasing decisions by providing key information before users visit your website.
When implementing product markup, distinguish between product snippets (informational displays) and merchant listings (transactional displays). Product schema supports both use cases, but the implementation details vary depending on whether you’re selling products directly or providing product information.
Essential product schema properties include name, description, brand, SKU, price, availability, and review ratings. For variable products with multiple options (sizes, colors, etc.), use the offers property to specify different pricing and availability for each variation.
{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Product", "name": "Premium Widget", "description": "High-quality widget for professional use", "brand": { "@type": "Brand", "name": "Widget Co" }, "offers": { "@type": "Offer", "price": "299.99", "priceCurrency": "USD", "availability": "https://schema.org/InStock", "seller": { "@type": "Organization", "name": "Example Store" } }, "aggregateRating": { "@type": "AggregateRating", "ratingValue": "4.5", "reviewCount": "127" } }
Product schema also supports additional properties like warranty information, product dimensions, energy ratings, and more attributes specific to your product category. Including comprehensive product data increases your chances of appearing in relevant product-focused search features.
Article Schema
Article schema optimizes news articles, blog posts, and editorial content for enhanced search visibility and potential inclusion in Google News results. This markup helps search engines understand your content’s authorship, publication date, and topical focus.
Proper article schema implementation includes author markup with detailed contributor information, publication date stamps, and headline optimization. For news websites and content publishers, this markup is essential for appearing in news carousels and topical search features.
The headline property should match your page’s H1 tag, while the description property can provide additional context beyond the meta description. Include featured image markup to increase the likelihood of image inclusion in article-rich results.
Author schema within article markup should link to comprehensive author profiles with biographical information, expertise indicators, and social media profiles. This supports Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) evaluation criteria.
Publisher information within article schema helps establish content credibility and supports knowledge graph development. Include detailed organization markup for the publishing entity, with logo, contact information, and social media profiles.
Review Schema
Review schema displays star ratings and review summaries in search results, significantly increasing trust signals and click-through rates for businesses across all industries. This markup can be applied to individual product reviews, service reviews, or aggregate business ratings.
When implementing review schema, ensure compliance with Google’s quality guidelines to avoid penalties. Only mark up genuine reviews from real customers, and avoid incentivizing or manipulating review generation specifically for schema markup purposes.
Individual review markup should include reviewer information, review date, rating value, and review content. For aggregate ratings, calculate accurate averages based on actual review data and update the markup when new reviews are received.
Review schema can be combined with other schema types for maximum impact. Product reviews within product markup, local business reviews within local business schema, and article reviews within article markup all contribute to enhanced search result displays.
Monitoring review schema performance requires tracking both rich result appearances and click-through rate improvements. Use Google Search Console to identify review-related structured data issues and ensure consistent display of review information in search results.
Schema Markup Implementation Methods
Implementing schema markup involves choosing the right format for your technical setup and content management requirements. Three main formats are available, each with distinct advantages for different implementation scenarios and technical skill levels.
The choice between JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa affects both implementation complexity and long-term maintenance requirements. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each format helps you select the most appropriate approach for your specific situation.
JSON-LD (Recommended)
JSON-LD has become Google’s preferred format for schema markup implementation due to its separation from HTML content and ease of maintenance. This JavaScript-based format is added to the HTML head section without affecting the existing page structure or visual presentation.
The primary advantage of JSON-LD lies in its independence from page content. You can add, modify, or remove structured data without touching existing HTML elements, making it ideal for content management systems and dynamic websites where content changes frequently.
JSON-LD supports complex nested structures and multiple entity relationships within a single code block. This flexibility makes it suitable for comprehensive markup implementations that describe multiple related entities on a single page.
Here’s a complete JSON-LD example for local business markup:
<script type="application/ld+json"> { "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "LocalBusiness", "name": "Downtown Coffee Shop", "address": { "@type": "PostalAddress", "streetAddress": "456 Main Street", "addressLocality": "Downtown", "addressRegion": "CA", "postalCode": "90210", "addressCountry": "US" }, "geo": { "@type": "GeoCoordinates", "latitude": "34.0522", "longitude": "-118.2437" }, "openingHours": [ "Mo-Fr 07:00-18:00", "Sa 08:00-16:00", "Su 09:00-15:00" ], "telephone": "+1-555-123-4567", "priceRange": "$$" } </script>
JSON-LD also integrates seamlessly with content management systems and can be generated dynamically based on page content. This makes it particularly suitable for large websites with thousands of pages requiring schema markup.
Microdata and RDFa
Microdata and RDFa represent inline markup formats that tag existing HTML elements with schema properties. While more complex to implement than JSON-LD, these formats provide tighter integration between markup and content, ensuring perfect synchronization between visible content and structured data.
Microdata uses HTML attributes like itemscope, itemtype, and itemprop to define schema properties directly within existing page elements. This approach guarantees that markup accurately represents visible content but requires more careful implementation to avoid HTML validation issues.
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) offers more advanced semantic web integration capabilities than Microdata, supporting external vocabulary linking and complex entity relationships. However, its complexity makes it less suitable for typical SEO applications compared to JSON-LD or Microdata.
When to choose Microdata or RDFa over JSON-LD:
- Legacy systems where JSON-LD integration is difficult
- Content where perfect markup-content synchronization is critical
- Advanced semantic web applications requiring external vocabulary linking
- Situations where you need to validate HTML semantics alongside structured data
Both formats require more technical expertise to implement correctly and maintain over time. Changes to page content often necessitate corresponding markup updates, increasing the risk of inconsistencies between visible content and structured data.
Step-by-Step Schema Implementation Guide
Successful schema markup implementation requires systematic planning, careful execution, and ongoing monitoring. This comprehensive approach ensures maximum SEO benefit while avoiding common pitfalls that can result in penalties or ineffective markup.
The implementation process involves multiple stages, from initial content audit through deployment and performance monitoring. Each stage builds upon previous work, creating a comprehensive structured data strategy that supports your overall SEO efforts.
Planning Your Schema Strategy
Begin your schema implementation by auditing existing content to identify high-impact opportunities for structured data markup. Focus on pages that already perform well in organic search or represent important conversion paths for your business.
- Prioritize schema implementation based on potential impact and available resources. Homepage, contact pages, product pages, and primary service pages typically offer the highest return on investment for schema markup efforts.
- Research competitor schema implementations using SEO tools like Screaming Frog, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to identify gaps in your current approach. Understanding how competitors use structured data reveals opportunities for differentiation and improvement.
- Create a schema roadmap that aligns with your business goals and technical capabilities. Start with foundational schemas like organization markup, then expand to page-specific schemas based on content type and user intent.
- Document your schema strategy to ensure consistent implementation across your entire website. Include guidelines for different page types, required properties for each schema type, and quality assurance procedures to maintain markup accuracy.
Creating Schema Markup
Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper provides an excellent starting point for beginners who need guidance creating their first schema implementations. This free tool generates basic markup code that you can customize for your specific needs.
Schema markup generators like those from Schema.dev and TechnicalSEO.com offer more advanced functionality for creating complex markup structures. These tools support multiple schema types and can generate code for different implementation formats.
For advanced customization requirements, manual JSON-LD creation provides complete control over markup structure and properties. This approach requires deeper technical knowledge but offers maximum flexibility for complex entity relationships and custom implementations.
WordPress users can leverage plugins like RankMath, Yoast, and Schema Pro for automated schema generation. These tools integrate with your content management system to generate structured data based on page content and site configuration.
Regardless of your chosen creation method, always validate generated markup before deployment. Use multiple testing tools to ensure code quality and compliance with Google’s structured data guidelines.
Testing and Validation
Google Rich Results Test serves as the primary validation tool for testing schema markup eligibility for rich snippets and enhanced search result features. This tool identifies markup errors and provides specific guidance for resolving issues.
The Schema.org Validator offers comprehensive syntax error detection for all schema types, including those not supported by Google’s rich results. Use this tool to ensure markup accuracy and compliance with Schema.org standards.
Google Search Console monitoring provides ongoing oversight of structured data performance after implementation. Regular review of structured data reports helps identify new issues and track the effectiveness of your markup strategy.
Advanced SEO tools like Screaming Frog and SEMrush offer automated schema auditing capabilities for large websites. These tools can crawl your entire website to identify missing markup, syntax errors, and optimization opportunities.
Establish a regular auditing schedule to maintain schema markup quality over time. Content changes, site updates, and evolving schema standards require ongoing attention to ensure continued effectiveness.
Implementation
Adding schema markup to your website can seem like a daunting task, but there are a few standard approaches. Each method has strengths and weaknesses, but the best choice will be the one that fits your use case the best.
Direct HTML injection involves adding JSON-LD scripts directly to your page source code, providing complete control over markup placement and structure. This method works well for static websites or situations where you need precise control over structured data implementation.
Google Tag Manager deployment offers a non-technical solution for implementing schema markup across your website. This approach allows marketing teams to manage structured data without requiring developer resources for each update or addition.
WordPress plugin integration using RankMath, Yoast, or dedicated schema plugins provides automated schema generation based on your content and site structure. These solutions handle technical implementation details while allowing customization for specific business needs.
Content management system-specific solutions for Shopify, Drupal, and other platforms often include built-in schema support or specialized extensions. Research available options for your specific CMS to find the most appropriate implementation approach.
Choose your implementation method based on technical resources, maintenance requirements, and the complexity of your schema markup needs. Consider long-term sustainability when selecting an approach, as schema markup requires ongoing maintenance and updates.
Schema Markup Best Practices and Guidelines
Following Google’s Quality Guidelines is essential for avoiding penalties and maintaining rich result eligibility. These guidelines emphasize accuracy, relevance, and user value as core principles for effective schema markup implementation.
Ensure your markup accurately represents page content without marking up information that isn’t visible to users. Schema markup should enhance, not replace, good content and user experience design principles.
Avoid marking up content not visible to users, as this violates Google’s guidelines and can result in manual actions against your website. All structured data should correspond to actual page content that provides value to visitors.
Keep structured data updated with content changes to maintain accuracy and avoid misleading search engine interpretation. Outdated markup can harm your search visibility and user experience.
Use specific schema types rather than generic ones whenever possible. More specific markup provides greater value to search engines and increases your chances of triggering relevant rich result features.
Common mistakes to avoid include:
| Mistake | Impact | Solution |
| Marking up invisible content | Penalty risk | Only mark up visible content |
| Using incorrect schema types | Reduced effectiveness | Research appropriate types |
| Outdated markup properties | Poor performance | Regular auditing and updates |
| Inconsistent data across pages | Confusion for search engines | Standardize markup approach |
| Over-marking content | Decreased quality signals | Focus on high-value markup |
Implement markup gradually rather than attempting comprehensive coverage immediately. Start with your most important pages and schema types, then expand systematically based on performance data and available resources.
Monitor search engine algorithm updates that affect structured data handling. Google regularly updates its approach to processing schema markup, and staying informed helps you adapt your strategy accordingly.
Measuring Schema Markup Success
Tracking schema markup performance requires monitoring multiple metrics across different tools and platforms. Success measurement should focus on both technical implementation quality and business impact metrics that demonstrate ROI.
Google Search Console provides the most comprehensive view of structured data performance, including rich result appearances, error reports, and enhancement suggestions. Regular review of these reports helps identify optimization opportunities and maintain markup quality.
Click-through rate improvements represent the most direct business impact of schema markup implementation. Compare CTR performance for pages with rich results versus standard listings to quantify the value of your structured data efforts.
Rich result appearance tracking using tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs helps monitor your visibility in enhanced search features. These tools can track your performance in featured snippets, knowledge panels, and other rich result types over time.
Key performance indicators for schema markup success include:
- Rich result appearance frequency
- Click-through rate improvements for enhanced listings
- Organic traffic increases to pages with schema markup
- Search visibility improvements for target keywords
- Knowledge panel appearances for brand queries
Set up alerts for schema validation errors and warnings to address issues promptly. Automated monitoring helps maintain markup quality as your website grows and content changes.
Analyze organic traffic patterns to identify correlations between schema implementation and search performance. While schema markup isn’t a direct ranking factor, it can influence user behavior and indirectly impact organic traffic.
Benchmark your schema markup performance against industry standards and competitor implementations. Understanding relative performance helps identify areas for improvement and competitive advantages.
Calculate return on investment for your schema markup efforts by comparing implementation costs with traffic and conversion improvements. This analysis helps justify continued investment in structured data optimization.
Future of Schema Markup and AI Search
The evolution of generative AI and chatbot search results has dramatically increased the importance of schema markup for website visibility. AI-powered search engines rely heavily on structured data to understand content relationships and provide accurate information in generated responses.
Google’s Search Generative Experience and similar AI search features use schema markup to identify authoritative sources and attribute information correctly. Websites without proper structured data risk being overlooked in AI-generated search results and summaries.
Voice search optimization increasingly depends on schema markup to provide context for spoken queries. Smart devices and voice assistants use structured data to understand content relationships and deliver relevant information to users.
Emerging schema types for new content formats and technologies continue to expand the vocabulary available for markup implementation. Recent additions include schemas for virtual events, energy ratings, and subscription-based services, reflecting evolving web content needs.
Through 2026, schema markup trends will likely focus on:
- Enhanced integration with AI search experiences
- More sophisticated entity relationship mapping
- Expanded support for multimedia content types
- Integration with augmented reality and virtual reality applications
- Improved support for real-time data and dynamic content
Preparing for future search evolution requires staying current with Schema.org updates and search engine announcements. The schema markup landscape continues to evolve rapidly, and early adoption of new schema types often provides competitive advantages.
Knowledge graphs will become increasingly important for search visibility, making comprehensive entity markup essential for maintaining competitive positioning. Websites that establish clear entity relationships through schema markup will be better positioned for future search algorithm updates.
As search engines become more sophisticated in processing structured data, the quality and comprehensiveness of schema implementation will become increasingly important differentiators. Investing in robust schema markup strategies today prepares your website for the continued evolution of search technology.
The integration of schema markup with emerging technologies like blockchain verification and decentralized web protocols may create new opportunities for establishing content authenticity and authority. Staying informed about these developments helps you adapt your strategy as new possibilities emerge.
Schema markup represents a fundamental shift toward semantic web principles, where content meaning is explicitly defined rather than inferred. Understanding this broader context helps you implement more effective structured data strategies that align with long-term search engine development.
By implementing comprehensive schema markup strategies today, you position your website for success in the AI-driven search landscape of 2026 and beyond. The websites that invest in structured data now will enjoy sustained competitive advantages as search technology continues to evolve.
Ready to Put Schema to Work for Your Website?
Schema markup is one of the fastest ways to improve how your pages appear in search results and how AI tools interpret your content—but only if it’s implemented correctly and aligned with your goals.Wondering which schema types actually matter for your site?Schedule a 30-minute consultation with Timmermann Group, and we’ll help you identify where schema can improve visibility, eligibility for rich results, and AI-driven search features.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is schema markup?
Schema markup is structured data code added to HTML that helps search engines understand webpage content more effectively. This standardized vocabulary created by Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex transforms unstructured content into machine-readable data using key-value pairs.
Is schema markup still important?
Schema markup remains critical for SEO success in 2026, especially with the rise of AI-powered search experiences and generative search results. Websites with properly implemented structured data see 20-30% higher click-through rates compared to standard listings and better positioning in emerging search technologies.
Why is schema markup important for SEO?
Schema markup enhances search visibility by triggering rich results that display star ratings, prices, and other compelling details directly in search results. This improved presentation increases click-through rates while helping search engines understand content context for better query matching and rankings.
What is schema markup in local SEO?
Local business schema markup displays essential location-specific details like opening hours, contact information, and customer reviews in search results. This structured data is critical for local SEO success, directly impacting visibility in local search results, Google Maps, and “near me” queries.