SEO Audit: What to Know for Exceptional Results
If you’ve ever tried to improve your website’s visibility in search engines, someone has probably told you to “start with an SEO audit.” And while that advice isn’t wrong, it’s incomplete. The reality is more nuanced: sometimes you need a comprehensive SEO audit before making a single change, and sometimes you can start generating wins within days while the deeper analysis happens in the background.
This guide breaks down exactly what an SEO audit is, what tools you need, how to conduct one step-by-step, and—critically—how to know whether you should invest in a full audit or start with a leaner approach. At Timmermann Group, we’ve helped hundreds of businesses navigate this decision, and we’ve learned that the best path forward depends entirely on where you’re starting from.
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is a structured, point-in-time evaluation of your website’s performance across search engine optimization factors. It examines your site’s technical SEO infrastructure, on page elements, content quality, user experience, and off-page signals like your backlink profile to identify what’s working, what’s broken, and what’s missing.
At Timmermann Group, we treat audits as comprehensive “website health checks” that map technical issues directly to business outcomes like leads, revenue, and pipeline quality. A site crawl error isn’t just a red flag in a report—it’s a quantifiable loss in potential customers reaching your important pages. This business-first lens separates a useful audit from a document that collects dust.
A modern SEO audit in 2024 and beyond must address more than classic search results. With Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, and ChatGPT increasingly surfacing direct answers, your audit needs to evaluate how your brand appears in ai search contexts—not just where you rank for blue links.
Consider a B2B manufacturer we worked with recently. Their site had been online for years with steady but stagnant organic traffic. A thorough SEO audit revealed that their robots.txt file was inadvertently blocking critical product category pages from site crawlers, and content gaps meant they had zero visibility for “how to choose” comparison queries that their buyers were actively searching. Within 60 days of addressing these hidden SEO issues, they saw a 34% increase in qualified leads from google search.
That said, not every business needs to wait for a 100+ page audit report before improving their site. Many companies can begin generating quick wins while the deeper analysis runs in parallel. This is an important distinction, and one we’ll explore throughout this guide.
Key benefits of an SEO audit:
- Identifies technical SEO errors blocking search engines from crawling and indexing your site
- Reveals content gaps and opportunities to capture relevant keywords
- Pinpoints user experience issues hurting conversions and engagement
- Evaluates your website’s ranking potential against competitors
- Creates a prioritized roadmap for SEO efforts that drive measurable growth
- Establishes baselines to track SEO performance over time
Do You Really Need a Full SEO Audit to Start SEO?
No, you don’t always need a complete SEO audit before improving your site—especially if you’re starting from minimal SEO activity.
This might sound counterintuitive coming from an agency that offers audit services, but it’s the truth. A full audit is an investment of time and resources. For some businesses, that investment is essential. For others, it’s overkill when what they really need is to fix obvious technical issues and start building momentum.

When a Lightweight Discovery Is Enough
Several scenarios call for a leaner approach:
- New site launch: You have a fresh website with limited content and no SEO history. There’s simply not enough data to justify an exhaustive audit. Start with foundational optimization and build from there.
- Obvious technical blockers: Your robots.txt is blocking your entire site, you have no XML sitemap submitted to google search console, or you’re still on HTTP instead of HTTPS. Fix SEO issues you can see before hunting for the ones you can’t.
- No prior SEO strategy: If you’ve never done systematic search engine optimization, a quick diagnostic will surface the 80% of high-impact issues that matter most. Research suggests that quick audits using free SEO tools like Google Search Console and a free crawler can identify the majority of critical problems in under two hours.
When a Full Audit Is Essential
A comprehensive SEO audit becomes critical when:
- Large enterprise sites: If you have 10,000+ URLs across multiple pages, you need systematic analysis to avoid missing critical problems buried in scale.
- Multi-location businesses: Companies with location-specific pages across dozens of markets need structured audits to identify inconsistencies in local visibility and NAP data.
- Site migrations or redesigns: Moving to a new domain, restructuring your site structure, or launching a redesign without a technical SEO audit is asking for traffic losses.
- Algorithm recovery: If your site took a hit from the March 2024 Core Update or similar, you need a deep dive into content quality and E-E-A-T signals before you can recover.
- Stalled growth despite ongoing work: When SEO efforts aren’t producing results, a site audit helps diagnose whether the problem is execution, strategy, or competitive positioning.
A Phased Approach That Works
At Timmermann Group, our typical approach involves a brief diagnostic “SEO triage” to unlock quick wins while deeper audit work runs in parallel. Here’s how that typically breaks down:
| Phase | Timeline | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Triage | Week 1–2 | Fix crawl and indexing blockers, verify GSC/GA4, address critical technical errors |
| Foundation | Month 1–2 | Optimize key pages for page optimization, improve local search visibility, set tracking baselines |
| Expansion | Month 3+ | Broader audit insights inform content strategy, link building, and site architecture improvements |
Full SEO Audit vs. Lean SEO Assessment:
| Factor | Full SEO Audit | Lean SEO Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Comprehensive analysis of entire website | Identify and fix high-impact issues quickly |
| Timeline | 4–8 weeks | 1–2 weeks |
| Best for | Large sites, migrations, recovery scenarios | New sites, obvious blockers, starting SEO programs |
| Deliverable | Detailed report with prioritized recommendations | Focused action list for immediate implementation |
| Investment | Higher upfront, long-term strategic value | Lower upfront, faster time-to-results |
What Tools Do You Need for an SEO Audit?
A professional website audit in 2024 requires a stack of tools that cover different aspects of SEO analysis. Here’s what you need and what each category contributes:
Essential Tools for Any SEO Audit:
- Google Search Console (GSC): Your primary window into how Google sees your site. Use it to check indexing status, identify technical SEO issues, monitor Core Web Vitals, and see which queries drive impressions and clicks. This is a free SEO checker that every business should have configured.
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4): Connects SEO visibility to actual business outcomes. Track organic traffic, engagement metrics, and conversions to measure the impact of optimization work. Use it alongside google analytics reports to understand user behavior on individual web pages.
- Crawling Tool (Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, or similar): Simulates how search engines crawl your entire site. Identifies broken links, redirect chains, missing meta tags, duplicate content, and other technical errors that a manual review would miss. Screaming Frog’s free tier crawls up to 500 URLs—sufficient for many small businesses.
- Rank Tracker: Monitors search rankings for your target keywords over time. Essential for measuring whether optimization work is moving the needle on search engine results pages.
- Backlink Analyzer (Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz): Evaluates your backlink data, including referring domains, link quality, anchor text distribution, and sites linking to your competitors but not you. A healthy backlink profile correlates strongly with higher search visibility.
- Page Experience Tools (PageSpeed Insights, GSC Core Web Vitals report): Measures site speed and core web vitals performance. These metrics directly impact both search rankings and user experience.
Agency-Grade Tools We Use at Timmermann Group:
As a full-service agency, we combine data from multiple paid suites to create decision-ready reports:
- Semrush or Ahrefs: For competitive analysis, keyword gap research, and comprehensive SEO audit tool capabilities that analyze site health at scale
- Looker Studio: To build custom dashboards connecting GSC, GA4, and other data sources into a single view of SEO performance
- Similarweb: For competitive traffic analysis and market benchmarking
- Specialized AI visibility tools: To monitor how your brand appears in AI-generated search results
A basic in-house audit can start for free with GSC, GA4, and a free crawler. But deeper SEO analysis typically benefits from agency-grade tools that provide broader context and competitive intelligence.
Step-by-Step SEO Audit Checklist
This section provides a complete SEO audit checklist broken into clear phases. Each step includes what to check, how to check it, and what healthy versus problematic states look like.
The goal isn’t just to run tools and generate reports. It’s to produce actionable findings that a marketer or web manager can interpret and prioritize. Let’s work through each phase systematically.
Technical Foundations: Can Search Engines Access and Understand Your Site?
Before evaluating content or links, you need to confirm that search engines can actually reach, crawl, and understand your web pages. This is where a technical audit begins.
Crawlability Checklist:
- Robots.txt review: Check that your robots.txt file isn’t blocking key pages from site crawlers. Access it at yoursite.com/robots.txt. Confirm that important sections (services, products, blog, location pages) are not disallowed.
- XML sitemap verification: Ensure you have a valid sitemap submitted to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. The sitemap should include all important pages and exclude pages you don’t want indexed (like thank-you pages or internal search results).
- HTTP status codes: Use a crawler like Screaming Frog to scan your entire site for status codes. You want to see mostly 200s (success). Flag any 4xx errors (broken pages), 5xx errors (server issues), or excessive 3xx redirects (redirect chains).
- Canonical consistency: Verify that your site has a single canonical version—either www or non-www, and always HTTPS. All variations should 301 redirect to the preferred version. Inconsistent canonicalization confuses search engines about which version to rank.
Technical Hygiene Checks:
- Staging environments: Confirm that development or staging sites are not indexable via robots.txt or server-level blocks. We’ve seen entire staging sites indexed and competing with production.
- Hreflang for international sites: If you serve multiple languages or regions, verify hreflang implementation is correct and reciprocal.
- Noindex usage: Audit pages with noindex tags to ensure you’re not accidentally blocking important pages from indexation.
- HTTPS and TLS: Confirm your entire site runs on HTTPS with a valid SSL certificate. A secure site is both a ranking factor and a trust signal for visitors.
- Server response time: Pages should respond in under 200ms. Slow server response indicates hosting or configuration issues that impact page speed across your entire website.
Crawl, Indexing, and Site Architecture
Once you’ve confirmed basic accessibility, evaluate how well search engines are actually indexing your site and whether your site structure supports discovery of key pages.
Indexing Analysis:
- GSC Index Coverage report: Compare “Indexed” versus “Excluded” URLs. Pay attention to patterns in exclusion reasons:
- “Crawled – currently not indexed” often indicates low-quality or thin content
- “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” signals canonicalization issues
- “Blocked by robots.txt” means you’re preventing crawling of those URLs
- Index bloat: Are pages indexed that shouldn’t be? Filter pages, paginated archives, and internal search results can waste crawl budget without providing value.
- Orphan pages: Identify important pages that have no internal links pointing to them. If search engines can’t discover a page through links, it’s unlikely to rank.
Site Architecture Review:
- Logical hierarchy: Your site should follow a clear structure: Home > Category > Subcategory > Individual Page. Users and search engines should be able to understand where they are and how pages relate.
- Click depth: Key pages should be reachable within 3 clicks from the homepage. Use your crawler to identify pages buried too deep in the site structure.
- Navigation audit: Review header navigation, footer links, and sidebar menus. Are your most important pages easily accessible? Are you linking to outdated or low-priority content prominently?
- Internal links mapping: Identify your top-value URLs (service pages, core product pages, lead-gen content) and verify they receive internal links from blogs, resources, and navigation hubs.
For example, a multi-location service business should group city pages clearly by state and metro, with internal links flowing from regional hubs to individual location pages. A user searching for “HVAC repair Kansas City” should land on a page that’s well-linked from both the main services section and a Missouri regional page.
On-Page SEO: Metadata, Headings, and Content Structure
An on-page SEO audit evaluates how well individual web pages are optimized for their target queries and user intent.
Metadata Checks:
- Title tags: Each page needs a unique, descriptive title between 50–60 characters. Front-load primary keywords where natural. Avoid duplicate titles across multiple pages.
- Meta descriptions: Write compelling descriptions between 150–160 characters that accurately summarize the page and encourage clicks. While not a direct ranking factor, meta descriptions significantly impact CTR in search results.
- Keyword alignment: Verify that page titles and descriptions align with the relevant keywords each page should target. Use GSC to see which queries already drive impressions to each page.
Content Structure:
- H1 usage: Each page should have one H1 that clearly describes the page topic. Multiple H1s or missing H1s create confusion for both users and search engines.
- Heading hierarchy: H2–H6 tags should create a logical outline of the content. Subheadings help users scan and help search engines understand content structure.
- Structured data: Identify opportunities for schema markup—Organization, LocalBusiness, Product, FAQ, Article, Breadcrumb. Use Google’s Rich Results Test to validate implementation.
- Internal anchor text: Links within your content should use descriptive anchor text (e.g., “St. Louis SEO services” rather than “click here”). This supports topical relevance and helps search engines understand linked page content.
Prioritization Tip: Focus your on page optimization on a sample of high-impact URLs first—typically your top 10–50 landing pages by traffic or revenue. Scale sitewide optimization after proving the approach works on your most important pages.
Content Quality, Search Intent, and E-E-A-T
Post-2024 Google updates have raised the bar significantly for content quality. Your audit must evaluate whether content meets the standards that now drive rankings.
Defining High-Quality Content:
- Depth and comprehensiveness: Does the content thoroughly answer the user’s question? Thin pages under 300 words rarely satisfy informational queries.
- Originality: Is the content unique, or is it recycled from other sources? Sites hit by recent algorithm updates often had content that added little value beyond what already existed.
- Author expertise: For topics where expertise matters (especially YMYL—Your Money, Your Life), is there a clear author with demonstrated knowledge? Author bios, about pages, and credentials signal trustworthiness.
- Freshness: Is content updated regularly? Outdated statistics, broken links, and obsolete recommendations hurt both rankings and conversions.
Intent Mapping:
Use GSC’s Performance report to identify pages with impressions but low CTR or poor average position. These are opportunities for improvement.
For each key page, determine search intent:
| Intent Type | User Goal | Content Format |
|---|---|---|
| Informational | Learn something | Guides, how-tos, educational content |
| Commercial | Compare options | Reviews, comparisons, best-of lists |
| Transactional | Take action | Product pages, service pages, pricing |
| Local | Find nearby | Location pages, maps, directions |
Ensure each page’s content matches its target intent. A service page shouldn’t read like a blog post, and an educational guide shouldn’t aggressively push sales.
E-E-A-T Signals:
- Visible author bios with credentials
- Comprehensive “About Us” page
- Trust signals: testimonials, case studies, certifications
- Third-party reviews on platforms like Google and industry directories
- Clear contact information and physical address
- Secure site (HTTPS)
Content Gaps and Cannibalization:
- Identify thin pages that should be merged or expanded
- Find duplicate content across multiple pages targeting the same keywords
- Map topic clusters to ensure you’re building comprehensive coverage around themes your business should own
- Flag obsolete content for updating or removal
User Experience, Core Web Vitals, and Site Speed
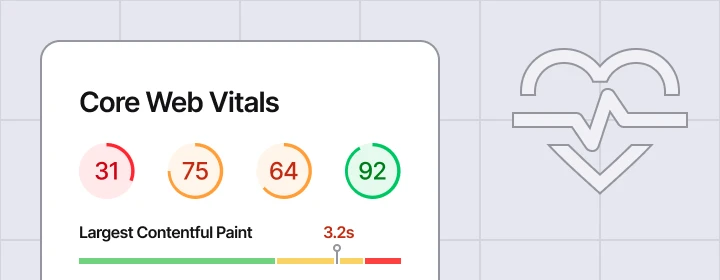
Google’s core web vitals are direct ranking signals, but more importantly, they correlate with user satisfaction and conversion rates. Sites passing Core Web Vitals see 24% lower bounce rates and 19% higher conversion rates.
Core Web Vitals Explained:
| Metric | What It Measures | Good Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | Loading speed—how fast the main content appears | Under 2.5 seconds |
| INP (Interaction to Next Paint) | Responsiveness—how fast the page responds to input | Under 200ms |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | Visual stability—how much the page shifts during loading | Under 0.1 |
Check these in GSC’s Page Experience report for field data (real user metrics) and PageSpeed Insights for lab data (simulated testing).
Common Fixes:
- Compress and properly size images
- Implement browser caching
- Reduce or defer unnecessary JavaScript
- Optimize web fonts (use font-display: swap)
- Upgrade hosting if server response times are consistently slow
Mobile Usability:
68% of online experiences are abandoned if page speed exceeds 3 seconds, and mobile devices now account for the majority of web traffic. Your audit must verify:
- Responsive design that adapts to all screen sizes
- Tap targets sized appropriately for fingers (at least 48×48 pixels)
- Readable font sizes without zooming
- No intrusive interstitials blocking content on smartphones
Connecting UX to Business Metrics:
Use GA4 to analyze behavior metrics alongside Core Web Vitals:
- Bounce rate and engagement rate by page
- Average session duration
- Conversion rate for key actions (form submissions, calls, purchases)
Better UX benefits both algorithmic rankings and actual business KPIs—not just an arbitrary SEO score. When we improve page speed for clients, we track both ranking changes and conversion improvements to demonstrate full ROI.
Off-Page SEO: Backlinks, Brand Signals, and Local Presence
Off-page factors—particularly external factors like backlinks and brand authority—remain critical ranking signals. Your audit should evaluate these elements systematically.
Backlink Profile Analysis:
Using a tool like Ahrefs or Semrush, evaluate:
- Referring domains: More unique domains linking to you generally correlates with higher authority. Focus on quality over quantity.
- Domain Rating (DR) or Domain Authority (DA): Sites with DR/DA above 50 are generally considered authoritative. Below 20 may indicate a weak link profile.
- Link velocity: Are you gaining or losing links over time? Sudden drops may indicate lost relationships or content becoming outdated.
- Topical relevance: Links from sites in your industry carry more weight than random directories.
- Anchor text distribution: Natural profiles have diverse anchor text. Heavy concentration on exact-match keywords can appear manipulative.
Identifying Risky Links:
- Spam scores above 5% warrant investigation
- Links from known link farms, PBNs, or unrelated sites
- Paid links without proper nofollow/sponsored attributes
- Links from hacked or compromised sites
Disavow is rarely necessary unless you have a history of manipulative link building or an obvious negative SEO attack. Google is generally good at ignoring low-quality links rather than penalizing for them.
Local SEO Audit (for local businesses):
- Google Business Profile: Verify accuracy of business name, address, phone (NAP), hours, categories, and description
- NAP consistency: Check that your NAP matches across 50+ directories and citations
- Reviews: Monitor review volume and sentiment on Google, Yelp, and industry-specific platforms
- Local content: Ensure you have optimized pages for each service area or location you serve
Brand Signals and Authority:
- Identify unlinked brand mentions that could become links
- Evaluate thought leadership content and its reach
- Review partnerships and sponsorships for link opportunities
At Timmermann Group, we turn this analysis into a prioritized outreach and digital PR plan rather than just flagging “toxic links” for removal.
AI Search, SERP Features, and Modern Visibility
The search landscape has shifted dramatically with the rise of AI-generated answers. Your audit must account for these new visibility opportunities.
AI Visibility Monitoring:
- Test your priority queries in Google AI Overviews and Bing Copilot
- Note whether AI responses cite your site, competitors, or neither
- Evaluate how accurately your brand and services are described in AI-generated content
Sites with strong topical authority appear in significantly more AI overviews. Building comprehensive content clusters positions you as a source these systems want to cite.
SERP Features to Audit:
| Feature | How to Earn It |
|---|---|
| Featured Snippets | Clear, concise answers formatted with lists, tables, or definitions |
| People Also Ask | FAQ-style content addressing related questions |
| Local Pack | Optimized Google Business Profile and local signals |
| Image Pack | Optimized images with descriptive alt text and file names |
| Video Results | YouTube content or properly marked up video embeds |
| Rich Results | Schema markup (FAQ, How-To, Product, Review) |
Strategic Mapping:
Map priority topics and relevant keywords to desired SERP features:
- FAQ schema for common customer questions
- How-to markup for tutorial content
- Video for complex explanations or demonstrations
- LocalBusiness schema for location pages
This connects back to your content strategy—understanding which features appear for your target queries informs what content formats you should create.
Turning Audit Findings Into an Action Plan
An audit is only valuable if it leads to decisions. Every issue identified needs a clear disposition: fix, improve, consolidate, create, or ignore.
Prioritization Framework:
We use an impact vs. effort matrix to categorize findings:
| Priority | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | Blocking indexing or conversions | robots.txt errors, broken internal links on key pages, HTTPS issues |
| High | Strong ranking/UX upside | Missing meta descriptions on high-traffic pages, slow page speed on conversion pages |
| Medium | Meaningful improvements | Internal linking optimization, schema implementation |
| Low | Nice-to-have | Minor meta tag tweaks, image compression on low-traffic pages |
Typical Phase 1 Actions (First 30 Days):
- Fix robots.txt and sitemap errors
- Implement HTTPS redirects if still on HTTP
- Repair top broken links (especially on important pages)
- Correct title tags on highest-traffic pages
- Address critical Core Web Vitals failures
Phase 2+ Actions (60–180 Days):
- Content consolidation and thin page remediation
- Content gaps and new content creation
- Link building and digital PR
- Advanced schema implementation
- Site architecture restructuring
Building Your Roadmap:
Create a simple SEO roadmap with specific timeframes and owners:
| Timeframe | Focus | Owner |
|---|---|---|
| 30 days | Critical technical fixes, quick wins | Development team |
| 90 days | On-page optimization, content improvements | Marketing team |
| 6 months | Link building, content expansion, advanced optimization | Agency + in-house |
At Timmermann Group, we pair this roadmap with Looker Studio dashboards connected to GA4 and GSC so stakeholders can monitor progress against KPIs in real-time.
When to Partner With an Agency for an SEO Audit
Some situations clearly call for professional support. Here are concrete triggers for bringing in a partner:
- Traffic or lead declines after a Google update: Diagnosing algorithm impacts requires experience and specialized tools
- Complex site migrations or redesigns: Moving URLs without proper planning destroys rankings; an agency brings migration expertise
- Multi-location or multi-language setups: Complexity multiplies with each location and language
- Stalled organic growth: When internal efforts aren’t producing results, fresh eyes identify blind spots
- Technical debt: Legacy sites with years of accumulated technical errors need systematic remediation
Advantages of Agency-Led Audits:
- Access to enterprise-grade SEO audit tool suites
- Cross-channel insight connecting SEO to PPC, UX/CRO, analytics, and email
- Experience interpreting nuanced data and prioritizing effectively
- Benchmarking against competitor and industry standards
At Timmermann Group, our audits integrate into a broader flywheel marketing approach. We tie SEO fixes to PPC efficiency, CRO improvements, and content strategy rather than operating in a silo. This means your website’s performance improvements compound across channels.
We offer flexible engagement models—from focused technical audit engagements to comprehensive strategic audits spanning SEO, web, and analytics. You don’t need to commit to a large, multi-month project to get started. A conversation or light assessment can help determine the right scope for your situation.
How to Start Improving SEO Today (Even Before a Full Audit)
You don’t need to wait for a complete audit report to start making progress. Here’s what you can do in the next 7–14 days:
Immediate Action Checklist:
- Verify GSC and GA4 are properly configured: If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it. Confirm both tools are collecting data correctly.
- Fix obvious 404 errors: Use GSC’s Pages report to find broken links and either restore content or redirect to relevant pages.
- Update title tags on your top 5 pages: Make them unique, compelling, and keyword-aligned.
- Refresh your most important service or product page: Add depth, update statistics, improve formatting, and ease search engines’ understanding of your expertise.
- Optimize your Google Business Profile: Ensure NAP accuracy, add photos, respond to reviews, and post updates.
- Check mobile usability: Load your site on mobile devices and note any obvious issues with navigation, readability, or speed.
- Set baseline benchmarks: Document current organic sessions, leads, and rankings for 10–20 target keywords so you can measure improvement.
Focus on What Matters Most:
Pick one or two key revenue-driving pages and make them “best in class” in content quality, UX, and conversion experience. A single high-performing page often outweighs dozens of mediocre ones.
Start the Conversation:
At Timmermann Group, our typical starting point is a free strategy call to review your site live, identify quick wins, and discuss whether a full audit is warranted. We’ll tell you honestly whether you need a 50-hour comprehensive analysis or a focused sprint on obvious opportunities.
The core message is simple: a thorough SEO audit is powerful, but you don’t have to wait for perfection to begin compounding gains. Starting small and iterating is often the most effective path to sustainable organic growth.
Ready to see where your site stands? Schedule a free 30min consultation call with our team, and we’ll help you determine the right next step—whether that’s a quick diagnostic or a deep dive into your site health.